×
![]()
graphdraw
| Type: | Model Group |
| Submitter: | Cézar Augusto Nascimento e Silva |
| Description: | In the Graph Drawing problem a set of symbols must be placed in a plane and their connections routed. The objective is to produce aesthetically pleasant, easy to read diagrams. As a primary concern one usually tries to minimize edges crossing, edges' length, waste of space and number of bents in the connections. When formulated with these constraints the problem becomes NP-Hard . In practice many additional complicating requirements can be included, such as non-uniform sizes for symbols. Thus, some heuristics such as the generalized force-direct method and Simulated Annealing have been proposed to tackle this problem. uses a grid structure to approach the Entity-Relationship (ER) drawing problem, emphasizing the differences between ER drawing and the more classical circuit drawing problems. presented different ways of producing graph layouts (e.g.: tree, orthogonal, visibility representations, hierarchic, among others) for general graphs with applications on different subjects. The ability to automatically produce high quality layouts is very important in many applications, one of these is Software Engineering: the availability of easy to understand ER diagrams, for model, can improve the time needed for developers to master database models and increase their productivity. Our solution approach involves two phases: (\\(i\\)) firstly the optimal placement of entities is solved, i.e.: entities are positioned so as to minimize the distances between connected entities; and (\\(ii\\)) secondly, edges are routed minimizing bends and avoiding the inclusion of connectors too close. We present the model for the first phase of our problem. |
Parent Model Group (graphdraw)
All other model groups below were be compared against this "query" model group.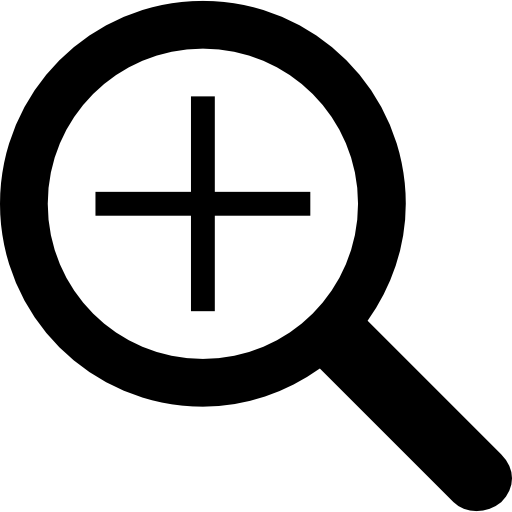  |
 |
|
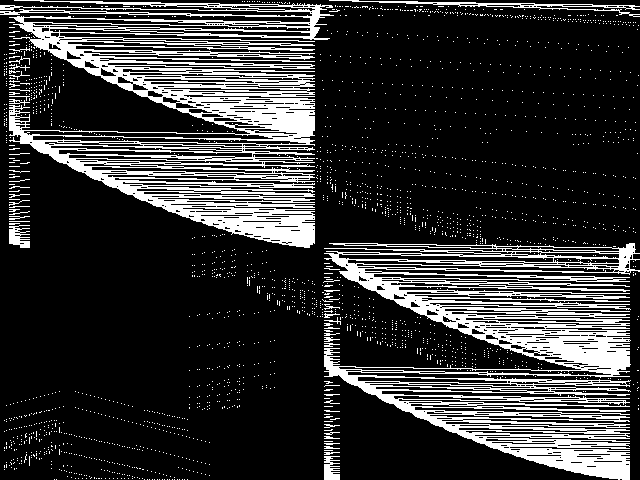
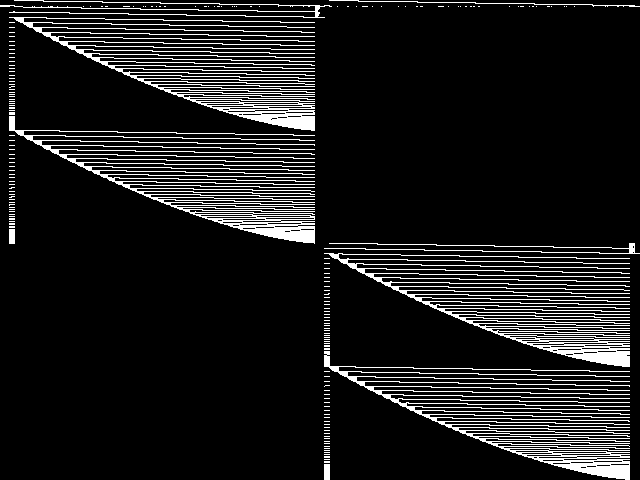
Model Group Composite (MGC) image
Composite of the decomposed CCM images for every instance in the query model group.
|
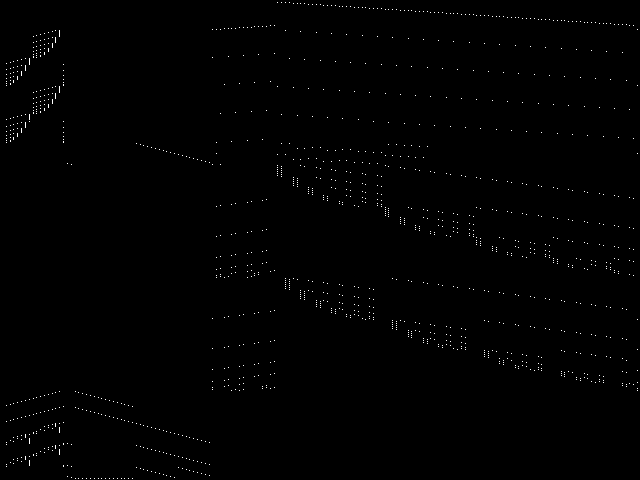
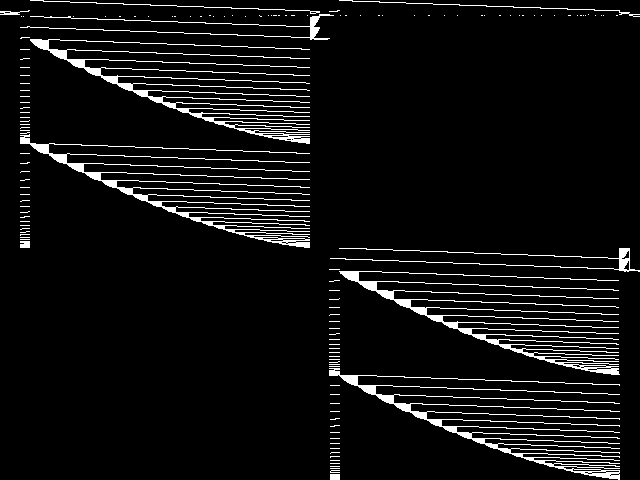
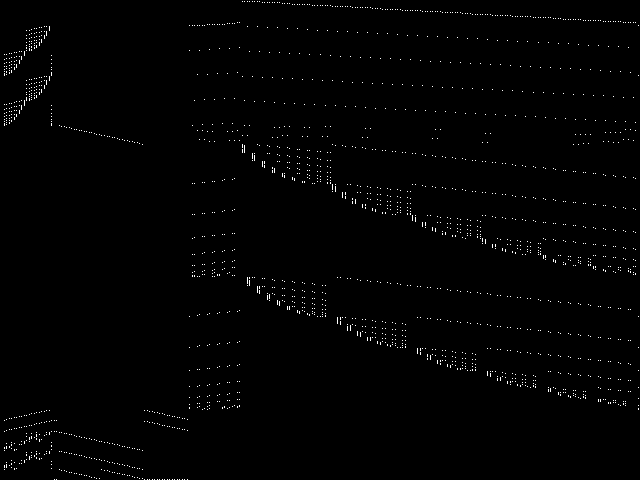
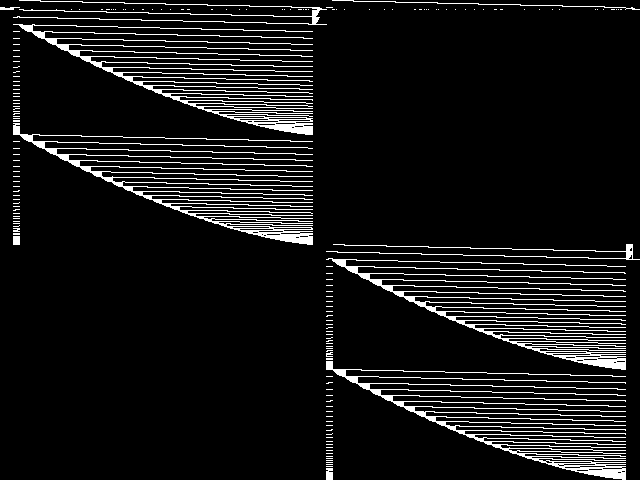
Component Instances (Decomposed)
These are the decomposed CCM images for each instance in the query model group.  |
These are component instance images.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Name | graphdraw-gemcutter | graphdraw-mainerd | graphdraw-domain | graphdraw-grafo2 | graphdraw-opmanager |
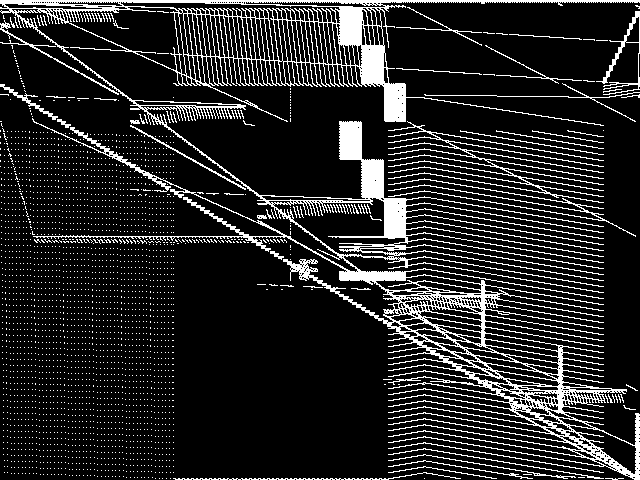
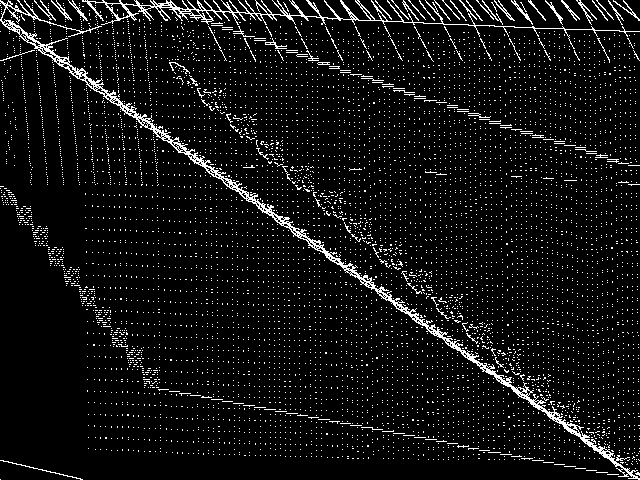
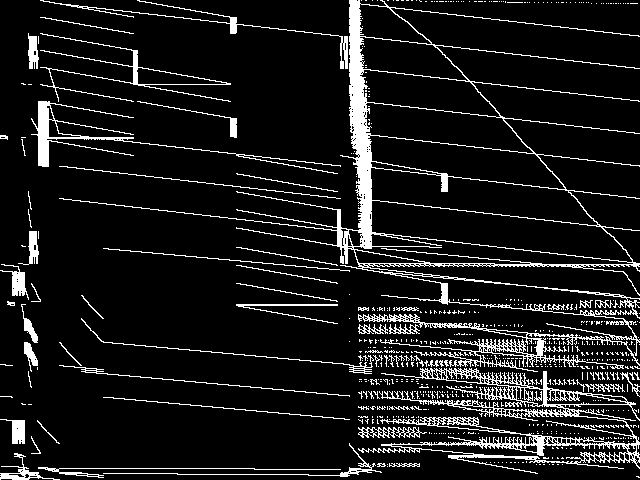
MIC Top 5 Model Groups
These are the 5 MGC images that are most similar to the MGC image for the query model group, according to the ISS metric.  |
FIXME - These are model group composite images.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Name | neos-pseudoapplication-62 | network_design | momentum | bab | maxfeassub | |
|
Rank / ISS
The image-based structural similarity (ISS) metric measures the Euclidean distance between the image-based feature vectors for the query model group and all other model groups. A smaller ISS value indicates greater similarity.
|
1 / 2.046 | 2 / 2.050 | 3 / 2.104 | 4 / 2.107 | 5 / 2.109 |
Model Group Summary
The table below contains summary information for graphdraw, and for the five most similar model groups to graphdraw according to the MIC.
| MODEL GROUP | SUBMITTER | DESCRIPTION | ISS | RANK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent Model Group | graphdraw | Cézar Augusto Nascimento e Silva | In the Graph Drawing problem a set of symbols must be placed in a plane and their connections routed. The objective is to produce aesthetically pleasant, easy to read diagrams. As a primary concern one usually tries to minimize edges crossing, edges' length, waste of space and number of bents in the connections. When formulated with these constraints the problem becomes NP-Hard . In practice many additional complicating requirements can be included, such as non-uniform sizes for symbols. Thus, some heuristics such as the generalized force-direct method and Simulated Annealing have been proposed to tackle this problem. uses a grid structure to approach the Entity-Relationship (ER) drawing problem, emphasizing the differences between ER drawing and the more classical circuit drawing problems. presented different ways of producing graph layouts (e.g.: tree, orthogonal, visibility representations, hierarchic, among others) for general graphs with applications on different subjects. The ability to automatically produce high quality layouts is very important in many applications, one of these is Software Engineering: the availability of easy to understand ER diagrams, for model, can improve the time needed for developers to master database models and increase their productivity. Our solution approach involves two phases: (\\(i\\)) firstly the optimal placement of entities is solved, i.e.: entities are positioned so as to minimize the distances between connected entities; and (\\(ii\\)) secondly, edges are routed minimizing bends and avoiding the inclusion of connectors too close. We present the model for the first phase of our problem. | 0.000000 | - |
| MIC Top 5 | neos-pseudoapplication-62 | Hans Mittelmann | Collection of anonymous submissions to the NEOS Server for Optimization | 2.045603 | 1 |
| network_design | MIPLIB submission pool | Imported from the MIPLIB2010 submissions. | 2.049581 | 2 | |
| momentum | T. Koch | Snapshot based UMTS planning problem, having a very wide dynamic range in the matrix coefficients and tending to be numerically unstable. Solved with Gurobi 4.5.1 on a 12-core Linux system in 3590.41 sec. | 2.103842 | 3 | |
| bab | Elmar Swarat | Vehicle routing with profit and an integrated crew scheduling like bab2 - bab5. Models differ in multi-commodity-flow formulation (path oder arc formulation) or time discretization and some are quite easy to solve while others (bab2, bab3 and bab6) are very difficult. | 2.106867 | 4 | |
| maxfeassub | Marc Pfetsch | Set covering problems arising from a Benders algorithm for finding maximum feasible subsystems. More details on the generation is given in the README file in the tarball. | 2.108610 | 5 |

