×
![]()
huefner
| Type: | Model Group |
| Submitter: | Falk Hueffner |
| Description: | The NP-hard Balanced Subgraph problem (variant of MaxCut) encoded as ILPs. Real-world models from two applications from bioinformatics, finding monotone subsystems in gene regulatory networks (http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10878-009-9212-2) and finding optimal layouts of tanglegrams (http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11269-0). |
Parent Model Group (huefner)
All other model groups below were be compared against this "query" model group.  |
 |
|
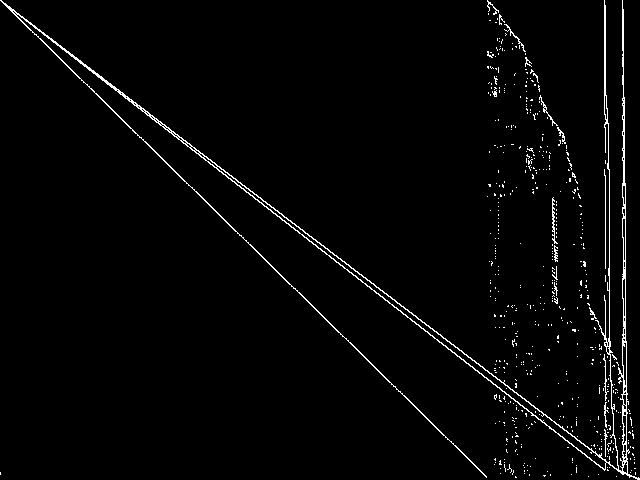
Model Group Composite (MGC) image
Composite of the decomposed CCM images for every instance in the query model group.
|
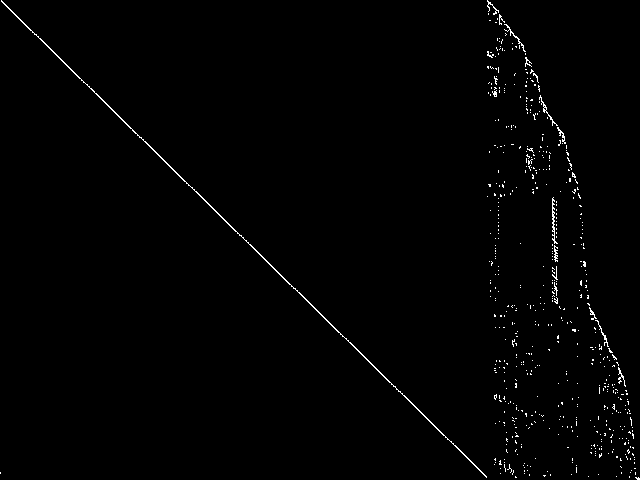
Component Instances (Decomposed)
These are the decomposed CCM images for each instance in the query model group.  |
These are component instance images.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Name | toll-like | tanglegram6 | tanglegram4 |
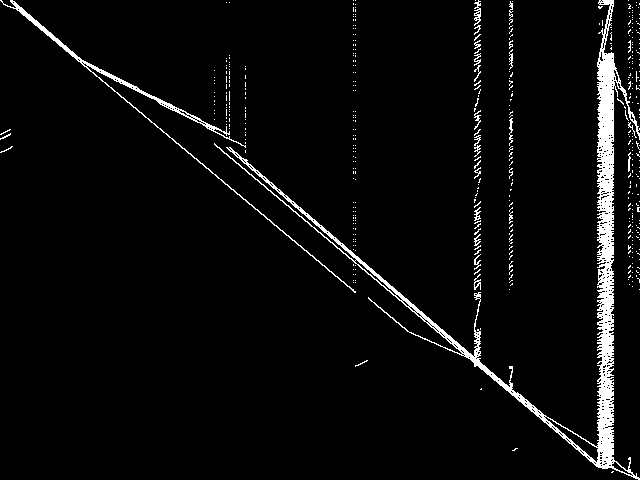
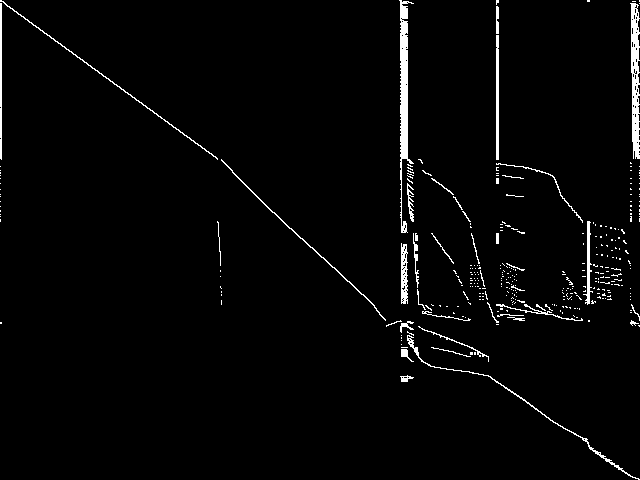
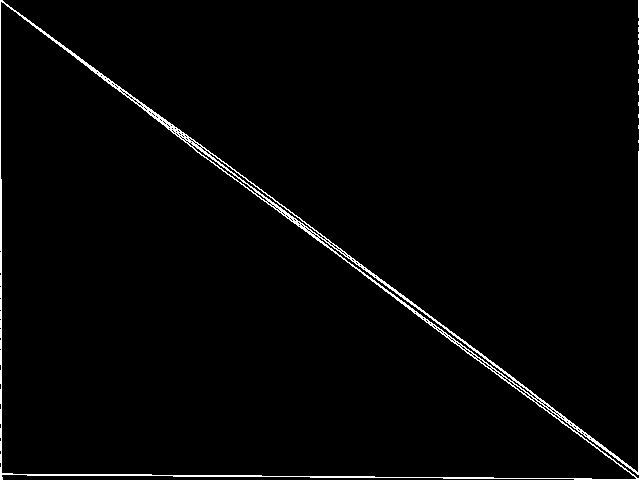
MIC Top 5 Model Groups
These are the 5 MGC images that are most similar to the MGC image for the query model group, according to the ISS metric.  |
FIXME - These are model group composite images.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Name | SiweiSun | lectsched | cryptanalysis | neos-pseudoapplication-109 | polygonpack | |
|
Rank / ISS
The image-based structural similarity (ISS) metric measures the Euclidean distance between the image-based feature vectors for the query model group and all other model groups. A smaller ISS value indicates greater similarity.
|
1 / 1.523 | 2 / 1.538 | 3 / 1.655 | 4 / 1.736 | 5 / 1.737 |
Model Group Summary
The table below contains summary information for huefner, and for the five most similar model groups to huefner according to the MIC.
| MODEL GROUP | SUBMITTER | DESCRIPTION | ISS | RANK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent Model Group | huefner | Falk Hueffner | The NP-hard Balanced Subgraph problem (variant of MaxCut) encoded as ILPs. Real-world models from two applications from bioinformatics, finding monotone subsystems in gene regulatory networks (http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10878-009-9212-2) and finding optimal layouts of tanglegrams (http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11269-0). | 0.000000 | - |
| MIC Top 5 | SiweiSun | Siwei Sun | These models come from my cryptographic research and are used to search for the best differential characteristics of the round-reduced versions of the block cipher Serpent with the mixed-integer programming technique. For all the models, including S1234.lp, S56701.lp, S456701.lp, I have found a feasible solution in the corresponding mst file. The challenge is that can we find better solutions or can we find the best solutions. | 1.523467 | 1 |
| lectsched | Harald Schilly | University lecture scheduling model | 1.537793 | 2 | |
| cryptanalysis | Gleb Belov | Linearized Constraint Programming models of the MiniZinc Challenges 2012-2016. I should be able to produce versions with indicator constraints supported by Gurobi and CPLEX, however don't know if you can use them and if there is a standard format. These MPS were produced by Gurobi 7.0.2 using the MiniZinc develop branch on eb536656062ca13325a96b5d0881742c7d0e3c38 | 1.654841 | 3 | |
| neos-pseudoapplication-109 | Jeff Linderoth | (None provided) | 1.736303 | 4 | |
| polygonpack | Antonio Frangioni | Given a set P of polygons, not necessarily convex, and a rectangle, we want to find the subset S of P with largest possible total area and a position every p in S so that there are no overlaps and they are all included in the rectangle. We allow a small set of rotations (0, 90, 180, 270 degrees) for every polygon. The problem is simplified w.r.t. the real application because the polygons do not have (fully encircled) "holes", which are supposedly filled-in separately, although they can have "bays". Models are saved as .lp. Model LpPackingModel_Dim means that we are trying to pack polygons taken from set ; there are currently 5 different sets, and is 7, 10 or 15. | 1.736607 | 5 |

